China actively seeks bilateral trade and investment deals outside of the World Trade Organisation. The government has put priority on forging agreements with neighbouring countries of Asia, but also many other countries on whom it relies for minerals, energy, food, infrastructure or geopolitical support.
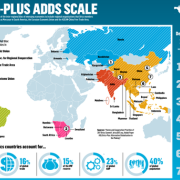
Beijing has signed bilateral trade agreements with ASEAN (2002), Hong Kong (2002), Macau (2003), Thailand (2003), Niger (2005), Chile (2006), Pakistan (2006), New Zealand (2008), Peru (2008), Singapore (2008), Costa Rica (2010), Taiwan (2010), Switzerland (2013), Iceland (2014), Australia (2015), Korea (2015), Georgia (2017), Maldives (2017) and the Eurasian Economic Union (2018). China is also a party to 127 bilateral investment treaties.
China is currently in bilateral negotiations with the European Union (investment), the Gulf Cooperation Council, Israel, Mauritius, Moldova, New Zealand (to upgrade the current agreement), Norway, Pakistan (upgrade), Singapore (upgrade), the Southern African Customs Union and Sri Lanka, as well as with Japan and Korea for a possible a three-way deal. Further down the horizon, there is talk of eventual negotiations with Canada, Chile (upgrade), Colombia, Fiji, Mexico, Mongolia, Nepal, Papua New Guinea, Palestine, Panama, Peru (upgrade), Switzerland (upgrade) and Uruguay.
Regionally, China has proposed a Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific, an initiative that would encompass the 21 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation nations, in direct rivalry with US-led projects like the Trans-Pacific Partnership. But that intitiative is currently on hold.
China is currently part of the talks on a Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). RCEP is a mega-regional trade agreement proposed by the Association of South East Asian Nations with its FTA partners : China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia and New Zealand.
If concluded, it would give Chinese corporations market access to India — in goods, services and investment — that it does not have through its own FTAs.
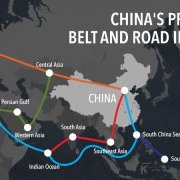
China also sees RCEP as a key element of its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), an infrastructure project meant to link Asia with Europe, passing through Africa, and with an extension to Latin America.
China is also using the BRI to push more countries to sign free trade agreements to consolidate the trade and investment leverage that the project opens up.
last update: June 2018
photo: Eddie / CC BY-ND 2.0